Stuffie Emotional Support Partners
connect bridges between children’s hearts and minds?

by Jodee Kulp
Emotional Development of a child provides confidence and strength as an adult. Healthy positive relationships without trauma allow children to develop compassion, empathy, and an understanding of right and wrong. They learn to trust.
Stuffies are filled with what Furry the Penguin calls “Stuffun-La-Muffins.”
Stuffies provide unbiased consistency by simply being available as a silent emotional support partner.
Emotional Support Partners are important in the development of children and actually help build skills in emotions, language, social skills and belief in the impossible.
Here are 4 ways a beloved Stuffie helps a child develop emotionally.
EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT
- Stuffie touch is powerful and cuddling with a soft Stuffies give children the touch of a friend. Children cuddle into the warmth and softness. Healthy soft touch provides a sense of peace.
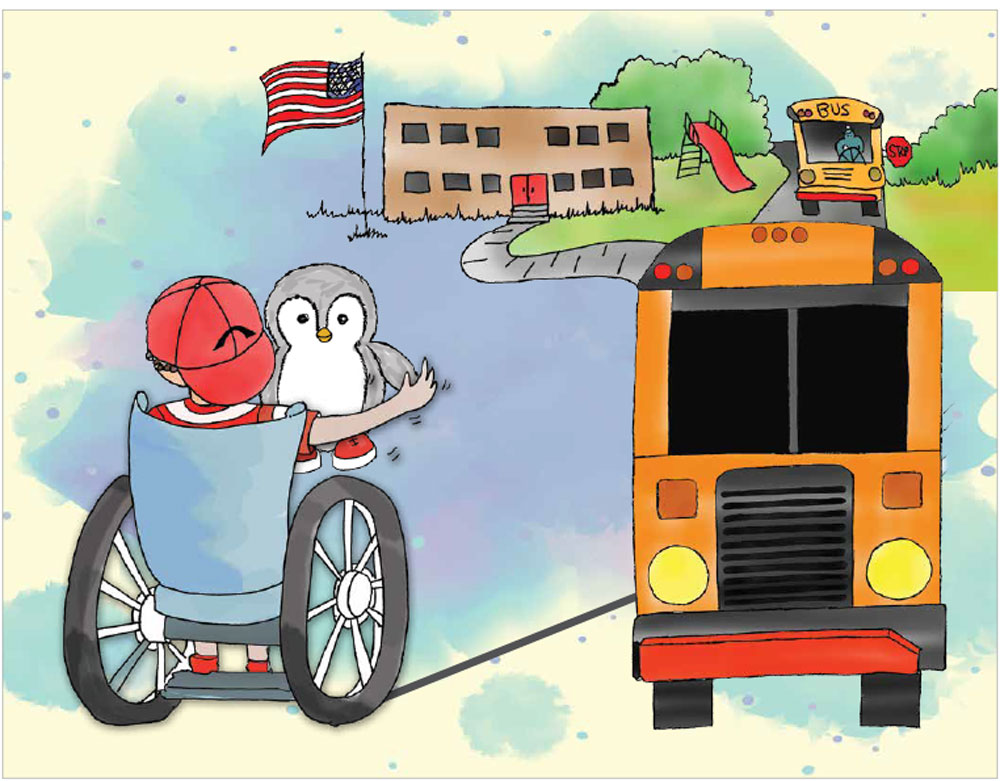
- Stuffies are calming. Stuffies can help children calm and soothe when life is hard. Stuffies can help distract from a painful experience or give a child courage to face a procedure. They can also become the training wheels to love a pet or as Furry did to connect with other children.
- Stuffies help self-soothe. Stuffies help a child self-soothe without the help of mom or dad or grandparents. Stuffies are a source of stress relief. Stuffies give emotional well being when life can be scary, strange or just new.
- Stuffied encourage development of empathy and compassion. Stuffies are loveable and children connect to them.
LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT
- Stuffies whisper ni
 ce things to children and help them work out unsolved problems by speaking the problem aloud plus children whisper nice things back to Stuffies. They practice positive and loving speech.
ce things to children and help them work out unsolved problems by speaking the problem aloud plus children whisper nice things back to Stuffies. They practice positive and loving speech. - Stuffies listen. Stuffies know how to remain quiet when a child is talking and not step on their thoughts or words. You can tell a story to a stuffie and they pay attention to every word.
- Stuffies are available. Stuffies never ignore a child when a child needs comfort. Stuffies do not take time to watch a sports show, talk on the phone, play video games or look at their cell phones. Unless Stuffies are pretending they are usually not busy with laundry, or work, or cleaning.
- Stuffies understand what you are saying. Stuffies know and understand the language of each special child.
SOCIAL SKILLS
- Stuffies understand acceptance. Stuffies help children test emotions. Sometimes we are kissed, pulled, and dropped. Stuffies are positive and they help increase the positive.
- Stuffies practice life skills. Stuffies are fed and put to bed. Stuffies play doctor and dentist, they ride buses, and trains, and go to school. They help build the responsibility of caring for another thing, remembering to pick it up and keeping track of a Stuffie so you do not lose your friend. Stuffies usually need care and attention daily especially in the early morning and going to bed times.
- Stuffies go places. Stuffies become the transitional object that allows a child to feel safe and connected in new or more challenging environments (doctors, hospitals, visiting others). Stuffies feed imaginations and are great at pretending.
- Stuffies are friends. Stuffies are friends that love you just for being you in all your good behavior and behavior others may not understand. Stuffies are often a child’s first playmate or the playmate available when friends return home.
BELIEVE IN THE IMPOSSIBLE – TOGETHER WE CAN!
- Stuffies provide possibilities. We can’t tell you why or how, but when a Stuffie becomes REAL to a child it increases – confidence, courage, and creativity.
- Stuffies create goal setting. Children learn to plan new events with stuffies. They can practice their events and then be more confident when working toward the goal. Stuffies encourage children to try new things.
- Stuffies reach inside. Somehow a Stuffie reaches the kindness of the heart of a child and from that kindness of Stuffun-la-Muffins – the child’s lovely heart emotions for nurturing another also grow.
- Stuffies are conversation starters. Stuffies help children say things they may be afraid to say alone and in Furry the Penguin’s case, started a whole Kindergarten talking with a a little boy who did not have words in school.
SOME OUTSIDE LINKS YOU MAY FIND INTERESTING
- How Stuffies can help adults – https://www.nytimes.com/2018/12/20/reader-center/adults-with-stuffed-animals.html
- Stuffed animal secrets – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hNpUBfbP2BE

 Furry The Penguin
Furry The Penguin
is a Member of the Aurora
Sweet and Softer Collection.
9.5″ PERKY PENGUIN –“Mac named him, FURRY”
Silky soft and sweet to the touch!